Early pregnancy monitoring is a topic that has generated a lot of questions from readers of this blog. Early pregnancies are usually monitored with a combination of serial blood tests and ultrasounds. At InVia Fertility Specialists, we will generally do a first pregnancy test (serum human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) level) approximately 15 days after egg retrieval (10 days after blastocyst transfer). We will check a repeat hCG level two days later and then do a first pregnancy ultrasound a week after. hCG levels have been discussed in detail in a previous blog. In the next few blog posts, we will now discuss the use of transvaginal ultrasound for diagnosing normal and abnormal pregnancy.
There can be some confusion about how gestational age is calculated. In naturally conceived pregnancies, gestational age is calculated from date of last menstrual period. So, when a woman misses her period she is already considered 4 weeks pregnant. Ovulation generally occurs two weeks prior to a missed menses. So in a cycle of conception, on the day of ovulation; the woman is considered two weeks pregnant.
In an assisted reproductive cycle, the day of egg retrieval is the day of ovulation. So, when we do a first pregnancy test approximately 2 weeks later; the patient is already considered 4 weeks pregnant!
The sequence of events in early pregnancy, as seen on transvaginal ultrasonography, follows a fairly predictable pattern.
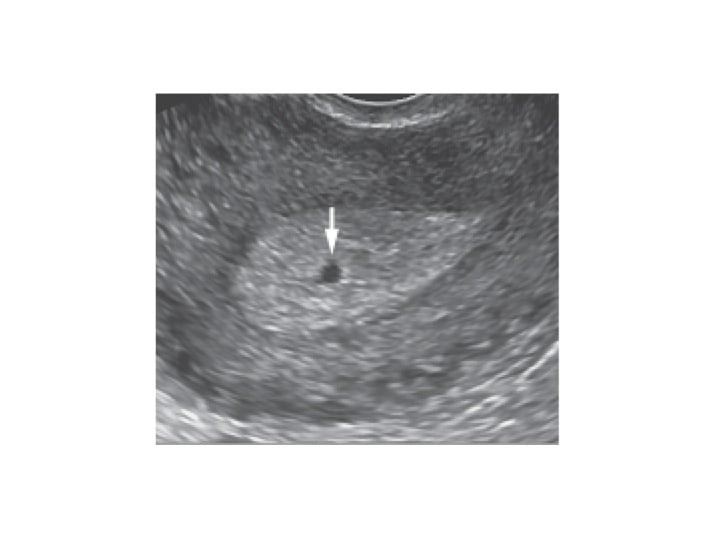
The gestational sac is first seen at approximately 5 weeks of gestational age, appearing as a small cystic-fluid collection with rounded edges and no visible contents, located in the central echogenic portion of the uterus (i.e., within the decidua). Any round or oval fluid collection in a woman with a positive pregnancy test should be reported as an intrauterine gestational sac (see Figure). Of interest is the fact that in some patients with a tubal pregnancy a similar appearing structure can be visualized (pseudogestational sac or decidual cyst).
The yolk sac, a circular structure about 3 to 5 mm in diameter, makes its appearance at about 5 ½ weeks of gestation.
The embryo is first seen adjacent to the yolk sac at about 6 weeks, at which time the heartbeat is present as a flickering motion. The length of the embryo (crown-rump length or CRL) can then be measured and it should show appropriate increase in follow up ultrasounds.
Thus, there is a sequence of events that occurs in a timely fashion in a normal pregnancy. When this sequence is not followed; the pregnancy is usually abnormal and the details will be discussed in a follow up blog.

Dr. Karande is Board Certified in the specialty of Obstetrics and Gynecology as well as the subspecialty of Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility. He is a Fellow of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and Member of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine.
Subscribe to our weekly blog digest

Entire Website © 2003 - 2020
Karande and Associates d/b/a InVia
Fertility Specialists

Comments