
 I have previously written a blog on how to improve your chances of success with fertility treatment.
I have previously written a blog on how to improve your chances of success with fertility treatment.
Improving your lifestyle is a big step in the right direction. Weight loss, regular exercise, quitting smoking tobacco and marijuana, drinking alcohol only in moderation are absolutely necessary to maximize chances of success.
A diet rich in anti-oxidants can also help. Great antioxidants include: blackberries, blueberries, strawberries, pomegranate, cranberries, green tea, dark chocolate, cooked vegetables and spices such as cumin, turmeric, ginger and oregano.
There has recently been a lot of interest in the use of antioxidants for improving semen parameters. Here is a brief summary of the details of these supplements and the rationale for using them.
Some background information first.
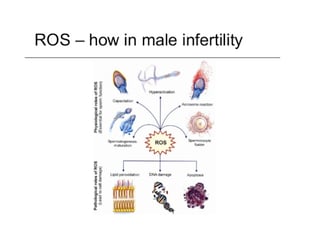
Oxidative stress (OS) is the imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) by the spermatozoa and white blood cells and the antioxidant capacity of the seminal plasma. Uncontrolled and excessive production of ROS overwhelms the limited antioxidant defenses in semen resulting in seminal oxidative stress.
The primary source of ROS production in infertile patients is the immature spermatozoa, damaged spermatozoa and white blood cells (granulocytes). Other sources of oxidative stress include infections of the male accessory glands (prostate, seminal vesicle, epididymis), smoking, varicocele, pollution, and drugs (marijuana).
There are natural antioxidant enzyme systems (catalase, glutathione peroxidase, superoxide dismutase). In healthy men, a delicate balance exists between physiological ROS and antioxidants in the male reproductive tract. The natural antioxidants protect the body from ROS damage. This permits normal oxidative metabolism to occur without damaging the cells, while still allowing for normal ROS-mediated cellular responses such as destruction of infectious pathogens and intracellular signaling. However, in conditions of oxidative stress, production of ROS overwhelms antioxidant defense.
They will restore balance by removing the ROS. This often results in improvements in the sperm count, motility and shape (morphology) and prevents DNA damage to sperm.
These include Coenzyme Q10 (Ubidecarenone), Lycopene (carotenoids), Omega 3 fatty acids, carnitine, Vitamin E and C, selenium, glutathione, N-acetyl cysteine, Zinc and Vitamin B12.
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ-10, ubiquinone, coenzyme Q, Ubidecarenone). This is a component of the electron transport chain and participates in aerobic cellular respiration, generating energy as ATP. In it oxidized form, it functions in the electron transport chain. In its reduced form, it functions as an antioxidant. In sperm cells, CoQ-10 is concentrated in the mitochondrial mid-piece, where it is involved in energy production. It also performs as an antioxidant, preventing lipid peroxidation of sperm membranes. A randomized controlled trial has confirmed that Co Q-10 showed significant increase in sperm motility, count and improvement in fertilization rate.
Lycopene – it is a bright red carotenoid pigment that is a powerful antioxidant. It is the most efficient quencher of oxygen and free radicals. Tomatoes are a good source of lycopene. It improves sperm concentration, motility and morphology (shape).
Omega-3 fatty acids. These include eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). DHA is essential for male fertility. Its deficiency is linked to low sperm count and infertility. Normal sperm cells contain an arc-like structure called the acrosome. Acrosome is critical in fertilization because it houses, organizes, and concentrates a variety of enzymes that sperms use to penetrate egg. DHA is essential in fusing the building blocks of the acrosome together. Without DHA, this vital structure does not form and sperm cells don’t work. DHA plays a major role in regulating membrane fluidity in sperm + regulation of spermatogenesis. Fish contain a lot of omega-3s.
Vitamin E and C. Vitamin E enhances sperm performance. It protects spermatozoa from oxidative damage and loss of motility. Vitamin C (calcium ascorbate) is a water-soluble ROS scavenger with high potency. It is a strong antioxidant destroying free radicals in the body and protects human spermatozoa against endogenous oxidative damage by neutralizing hydroxyl, superoxide and hydrogen peroxide radicals. Vitamin C prevents sperm agglutination. Vitamin C and E act together to protect against peroxidative attack on spermatozoa.
Vitamin B12. It is important in cellular replication, especially for synthesis of RNA and DNA. Deficiency states have been associated with decreased sperm count and motility.
Trace elements such as selenium and zinc etc.. Selenium is essential for formation of phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase – an enzyme present in spermatids, which becomes a structural protein comprising over 50% of the mitochondrial capsule in the mid-piece of mature spermatozoa. Deficiency leads to instability of the mid-piece resulting in defective motility, breakage of the spermatozoal mid-piece and increase morphological abnormalities, mostly affecting the sperm head. Zinc levels are generally lower in infertile men with diminished sperm count. Zinc supplementation shows improvement in sperm quality, motility, fertilization capacity and a reduction in the incidence of anti-sperm antibodies.
Co-Q 10 can be purchased over the counter at any of the major pharmacy chains. C-Q 10 and its metabolite (Ubiquinol) are available at Costco. These are 100 mg tablets and the dose is two tablets orally daily. Ubiquinol is also available in a liquid form and is supposed to be more easily absorbed. FertilityBlend for Men is a product manufactured by the Daily Wellness Company and available at GNC stores. It contains L-carnitine, folic acid, Vitamin C & E, green tea, selenium, Zinc, Vitamins B6 and B12. The dose is two tablets orally daily and it takes 60 – 90 days to see an improvement in sperm parameters.
Further details on male supplements can also be found at this website: www.lifechoicesandfertility.com

Entire Website © 2003 - 2020
Karande and Associates d/b/a InVia
Fertility Specialists
